RAG, or how to talk to our documents?
Discover how Retrieval Augmented Generation enables large language models (LLMs) to provide accurate answers based on expertise.

What does Retrieval Augmented Generation mean?
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) is a technique for enhancing the results of large language models using external data sources.
An example of a large language model (LLM) would be Chat GPT, LLaMA or GPT-4.
Using RAG in practice
Let’s assume that we want to build a chatbot that provides answers about certain knowledge in a niche area.
The knowledge we want to provide is so inaccessible that ChatGPT can’t answer the user’s questions. It answers that it doesn’t know or makes up facts.
To make our chat-bot work, we need a way to make it smarter. This is where RAG comes into play:
- We build our knowledge base:
- We collect, for example, 50 PDFs with specialized knowledge;
- We process each PDF, extracting text from it;
- We process the knowledge:
- We divide the documents into paragraph-sized parts;
- We process each part into a machine-readable format;
- We save the processed data in a vector database;
We need to divide our documents into smaller parts, because we are currently unable to feed the ChatGPT with the text of all 50 PDFs. For only one document the problem disappears :)
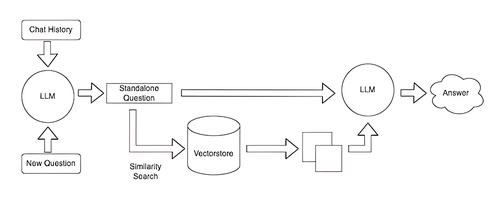
After creating the knowledge base once, we are able to reuse it for user responses. Let’s assume he directed a question to our chatbot “How to do complex thing X?”:
- We process the question into a machine-readable format.
- We look for the most matching document.
After finding the most matching document, we are able to query our language model:
Based on the given context, answer the user’s question. If the answer is not in the context, answer “I don’t know.”
Context: (our most matching document).
Question: how to do complex thing X?
LLM, in turn, can answer:
Complicated thing X is done by (answer based on information from documents).
Or admit that it doesn’t know:
I do not have access to such information.
That’s it! Retrieval Augmented Generation in practice :)
The devil is in the details
The above example is simplified, in order to introduce the concept.
Technical details:
- The questions for LLM are called “prompts”
- Text processing is called generating embeddings. This process is done using ML, for example SBERT models;
- We save the embeddings most commonly in a vector database;
- Embeddings allow us to perform semantic search, unlike traditional lexical search;
- The vector comparison process can be accelerated at the expense of search quality;
- Text fragments can partially overlap for better context.
Each of the above points can be described in great detail - the topic is very broad and, as of today, very rapidly developing!
If you are curious about this topic, I encourage you to expand your knowledge based on articles from Google :)
You can follow my blog with any

Maciej Kaszkowiak
I try to write about interesting things, such as artificial intelligence, created projects, and travel - see all posts.

Victory at HackYeah 2023!
On 30.09 - 01.10, we took 1st place out of 37 teams in the Health & Well-being track at HackYeah 2023, the largest on-site hackathon in Europe! 🏆

Eastern Poland by bike - adventure on two wheels
Beautiful views, wilderness camps and duct tape. Read about the cycling adventures of a thousand kilometers and eleven days of riding!

Hackathon, a source of rubber ducks and adrenaline
Do you associate being locked in a building for 48h with jail? Throw in free coffee, pizza and internet access, and people will lock themselves up voluntarily!